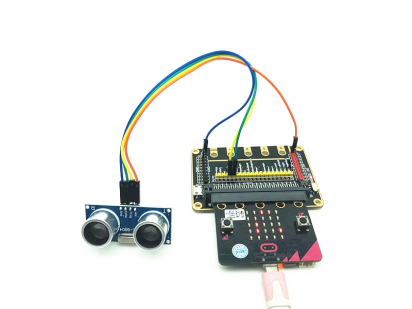
In this lesson, we will carry out an interesting experiment to control an ultrasonic sensor to measure distance with a Micro:bit.
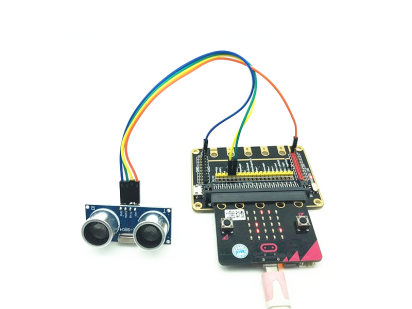
26.1 Components to be prepared
26.2 Ultrasonic distance sensor
26.2.1 Ultrasonic distance sensor
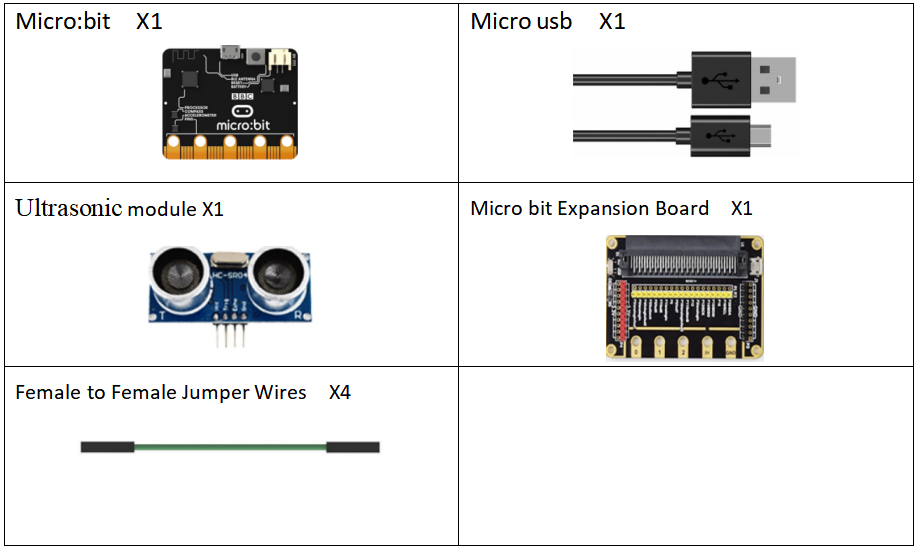
The model of the ultrasonic distance sensor we use is hc-sr04, it is mainly composed of two left and right probes, looking like our human eyes. One probe is responsible for transmitting sound waves for detection, and the other probe is responsible for receiving sound waves for return. It has 4 pins, which are VCC; Trig (control end - trigger signal input); Echo (receiver - recovery signal output); Gnd(ground).

26.2.2 The working principle of the Ultrasonic Distance Sensor
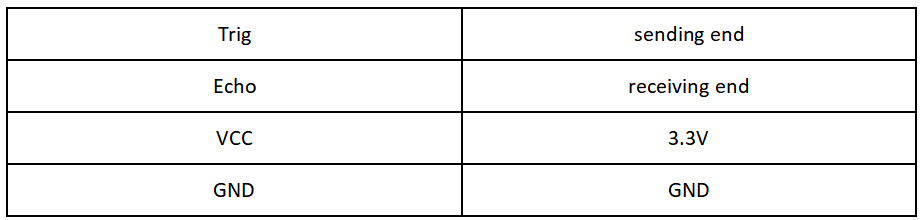
The method of detecting distance of ultrasonic wave is called echo detection method,which ultrasonic emitter emits to a certain direction, in the moment of timer timing starts at the same time, the ultrasonic wave in air, run into obstacles on the way your face (objects) block was reflected immediately, ultrasonic receiver received the ultrasonic reflected back to immediately stop timing. The propagation speed of ultrasonic wave in the air is 340m/s. According to the time t recorded by the timer, the distance s from the launch point to the obstacle surface can be calculated, that is, s=340t/2. Under this principle of ultrasound, ultrasonic ranging module is widely used in practical applications, such as car reversing radar, uav, and intelligent car.
26.3 Low level and high level
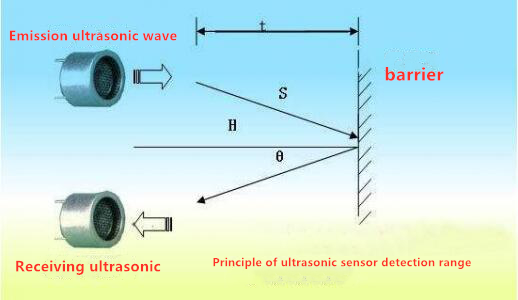
In circuit, the form of binary (0 and 1) is presented as low level and high level.
Low level is generally equal to ground voltage (0V). High level is generally equal to the operating voltage of components.
The low level of Micro:bit is 0V and high level is 3.3V, as shown below. When IO port on Micro:bit outputs high level, low-power components can be directly driven,like LED.
26.4 Circuit
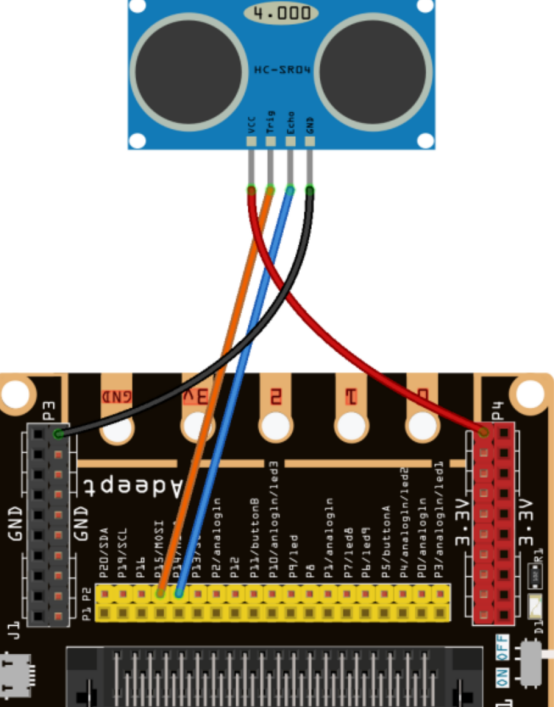
You should connect the components according to the following circuit diagram, and view the pictures with the function “Zoom in”: The pin Echo is connected to P14; the pin Trig is connected to P15.
26.5 MakeCode programming
Next, we will use the online MakeCode Editor to complete the experiment in this lesson.
26.5.1 Start programming
(1) Log in to the website
1. You need to enter the URL in the address bar of Google Browser:
https://makecode.microbit.org/
2. After the website is successfully opened, the interface as shown below will appear:
(2) Import a project
1. In the HOME interface, click the "Import" button to import the external ".hex" file:
In the pop-up dialog box, select the "Import File", as shown in the following figure:
Click the "Choose File"
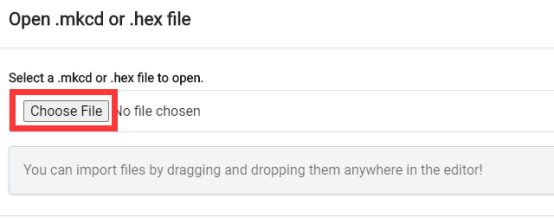
Find the code file for this lesson:
BBC _Microbit_Kit\Code\Lesson_26\BlockCode
Select the file in ".hex" format and click the Open:
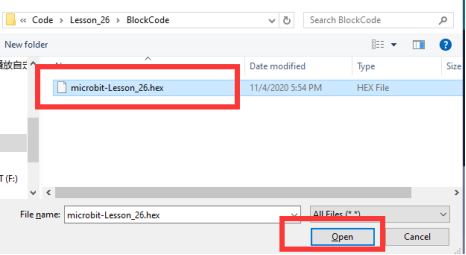
2. Notice whether the file has been loaded into the following window, and then click the "Go ahead!" button, as shown in the following figure:
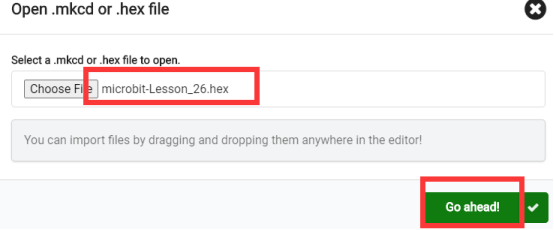
3.You can see the following interface when successfully opening the file:
26.5.2 Run the program
1. After the program is written, connect micro:bit and PC with a Micro USB cable.
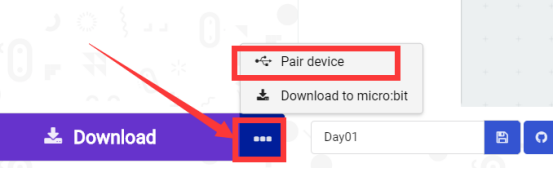
2. After micro:bit is connected to the computer, you need to first "Pair device". Click the  button on the right of
button on the right of  in the lower left corner, and then click the
in the lower left corner, and then click the  option, as shown in the following figure:
option, as shown in the following figure:
Then click  in the lower right corner
in the lower right corner
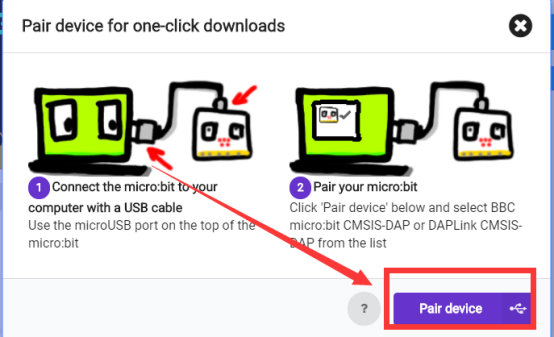
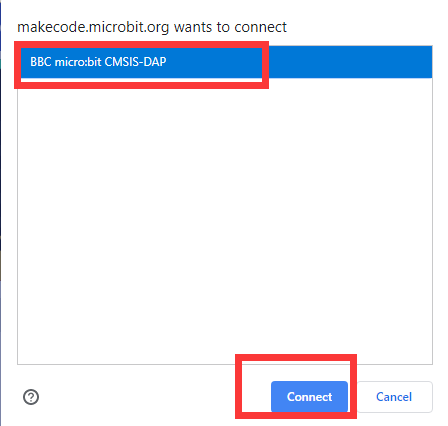
Then the following dialog box will pop up, select  , and then click
, and then click 
After the device is successfully paired, the  button changes to
button changes to 

3. Start to download the program to Micro:bit, and click the  button. Generally, the program will be downloaded directly to the Micro:bit. After the download is completed, your Micro:bit will restart and run the program just downloaded.The LED screen on the Micro:bit will show the distance data of the obstacles detected by the ultrasonic sensor, as shown in the following figure:
button. Generally, the program will be downloaded directly to the Micro:bit. After the download is completed, your Micro:bit will restart and run the program just downloaded.The LED screen on the Micro:bit will show the distance data of the obstacles detected by the ultrasonic sensor, as shown in the following figure:
[Note]
1.If the LED screen on the Micro:bit doesn’t show the distance data after clicking the button  , you need to click the
, you need to click the  button on the right of the
button on the right of the  , and then click the
, and then click the  , and observe the Micro:bit again, as shown in the following figure:
, and observe the Micro:bit again, as shown in the following figure:
2.If the LED screen still doesn’t show the distance data, you need to unplug and then plug in the USB cable connected to the Micro:bit, and then download the program again.
If you have problems, please send us an email: support@adeept.com
26.5.3 Learn the code program
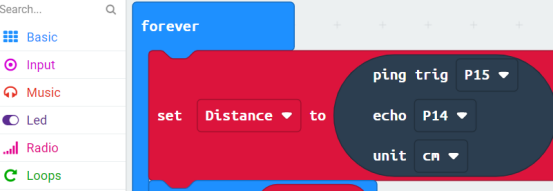
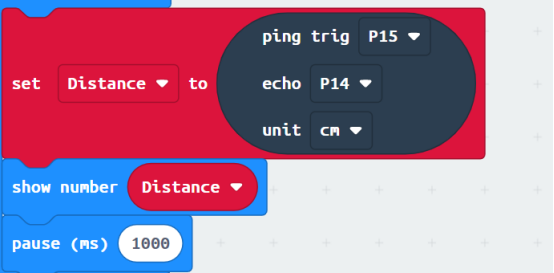
In the program, we use the following instruction block, which is explained as follows:

The distance of obstacles measured by the ultrasonic module will be assigned to the variable distance, and then displayed on Micro:bit of LED Screen. LED Screen refreshes every 1 second.
【Note】
If you want to import the “Sonar” expansion block in a new project, follow the steps below to add it.
(1)Click the button【Extensions】:
(2)Enter “Sonar”and click search.
(3)Select “Sonar”.
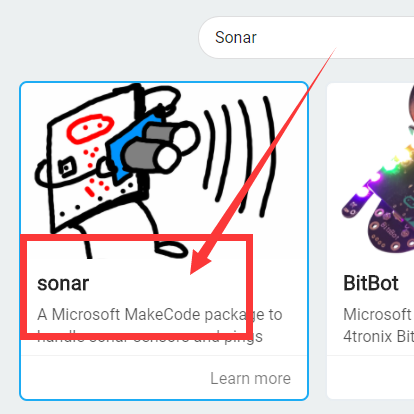
(4) Added successfully:

26.6 Python programming
26.6.1 Run the program
1.Connect micro:bit and PC with a Micro USB cable.
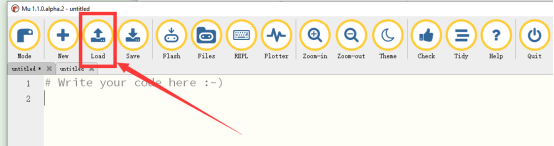
2. Open the Mu Editor installed on the computer, and click the button [Load] in the upper left corner to open the source code program of this lesson:
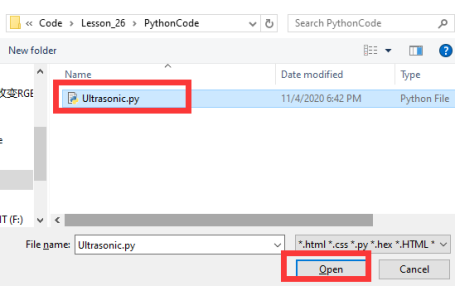
Find the code file for this lesson:
BBC _Microbit_Kit\Code\Lesson_26\PythonCode
Select the file in ".py" format and click the Open:
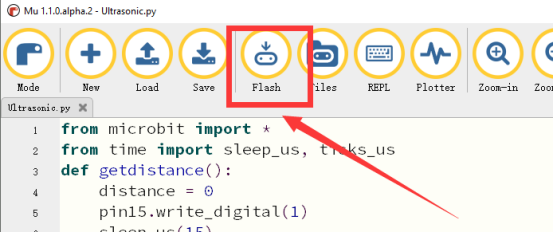
3.Click button【Flash】 to download the program to the Micro:bit. Click the button  immediately (click the button
immediately (click the button  when the Micro:bit indicator is flashing), and the output data will be read on the console, as shown below:
when the Micro:bit indicator is flashing), and the output data will be read on the console, as shown below:
4.After the program is downloaded, the LED screen on the Micro:bit will show the distance data of the obstacles detected by the ultrasonic sensor, as shown in the following figure:
If you have problems, please send us an email: support@adeept.com
26.6.2 Learn the code program
(1)The custom getdistance() function is used to get the distance between the obstacle and the ultrasonic module.The unit of return value is CM.
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | def getdistance(): distance = 0 pin15.write_digital(1) sleep_us(15) pin15.write_digital(0) while pin14.read_digital() == 0: pass if pin14.read_digital() == 1: ts = ticks_us() while pin14.read_digital() == 1: pass te = ticks_us() tc = te - ts print(te, ts) distance = (tc*170)*0.0001 return distance |
(2)The data detected by the ultrasonic sensor is shown on the LED screen of the Micro:bit.
20 21 22 23 | while True: distance = round(getdistance()) display.scroll(distance) sleep(500) |
getdistance():
Get the distance from the ultrasonic module to the obstacle. The unit is CM.