Overview
In this lesson, we will make a simple voltmeter (0~5V) with Arduino UNO and LCD1602. Then, we will measure the voltage of the potentiometer(when adjusting the knob) with the simple voltmeter and display the voltage detected on the LCD1602.
Components
- 1 * Arduino UNO
- 1 * USB Cable
- 1 * LCD1602
- 2 * Potentiometer
- 1 * Breadboard
- Several jumper wires
Principle
The basic principle of this experiment: Convert the analog voltage collected from Arduino to digital quantity by the ADC (analog-to-digital converter) through programming, and then display the voltage on the LCD1602.
Connect the three wires from the potentiometer to your Arduino board. The first goes to ground from one of the outer pins of the potentiometer. The second goes from analog input 0 to the middle pin of the potentiometer. The third goes from 5V to the other outer pin of the potentiometer.
By turning the shaft of the potentiometer, you change the resistance on either side of the wiper which is connected to the center pin of the potentiometer. This changes the voltage at the center pin. When the resistance between the middle and the side one (connected to 5V) is close to zero (and the resistance on the other side is close to 10k Ohm), the voltage at the middle pin is close to 5V. When the resistances are reversed, the voltage at the center pin changes to about 0V, or ground. This voltage is the analog voltage that you're reading as an input.
The Arduino UNO board has a circuit inside called an analog-to-digital converter that reads this changing voltage and converts it to a number between 0 and 1023. When the shaft is turned all the way in one direction, there are 0 volts going to the pin, and the input value is 0. When the shaft is done in the opposite direction, it's 5 volts going to the pin and the input value is 1023. In between, analogRead( ) returns a number between 0 and 1023 that is proportional to the amount of voltage being applied to the pin.
Key functions:
● analogRead()
Reads the value from the specified analog pin. The Arduino board contains a 6 channel (8 channels on the Mini and Nano, 16 on the Mega), 10-bit analog to digital converter. This means that it will map input voltages between 0 and 5 volts into integer values between 0 and 1023. This yields a resolution between readings of: 5 volts / 1024 units or, 0.0049 volts (4.9 mV) per unit. The input range and resolution can be changed using analogReference( ).
It takes about 100 microseconds (0.0001 s) to read an analog input, so the maximum reading rate is about 10,000 times a second.
Syntax:
analogRead(pin)
Parameters:
pin: the number of the analog input pin to read from (0 to 5 on most boards, 0 to 7 on the Mini and Nano, 0 to 15 on the Mega)
Returns:
int (0 to 1023)
Procedures
Step 1: Build the circuit
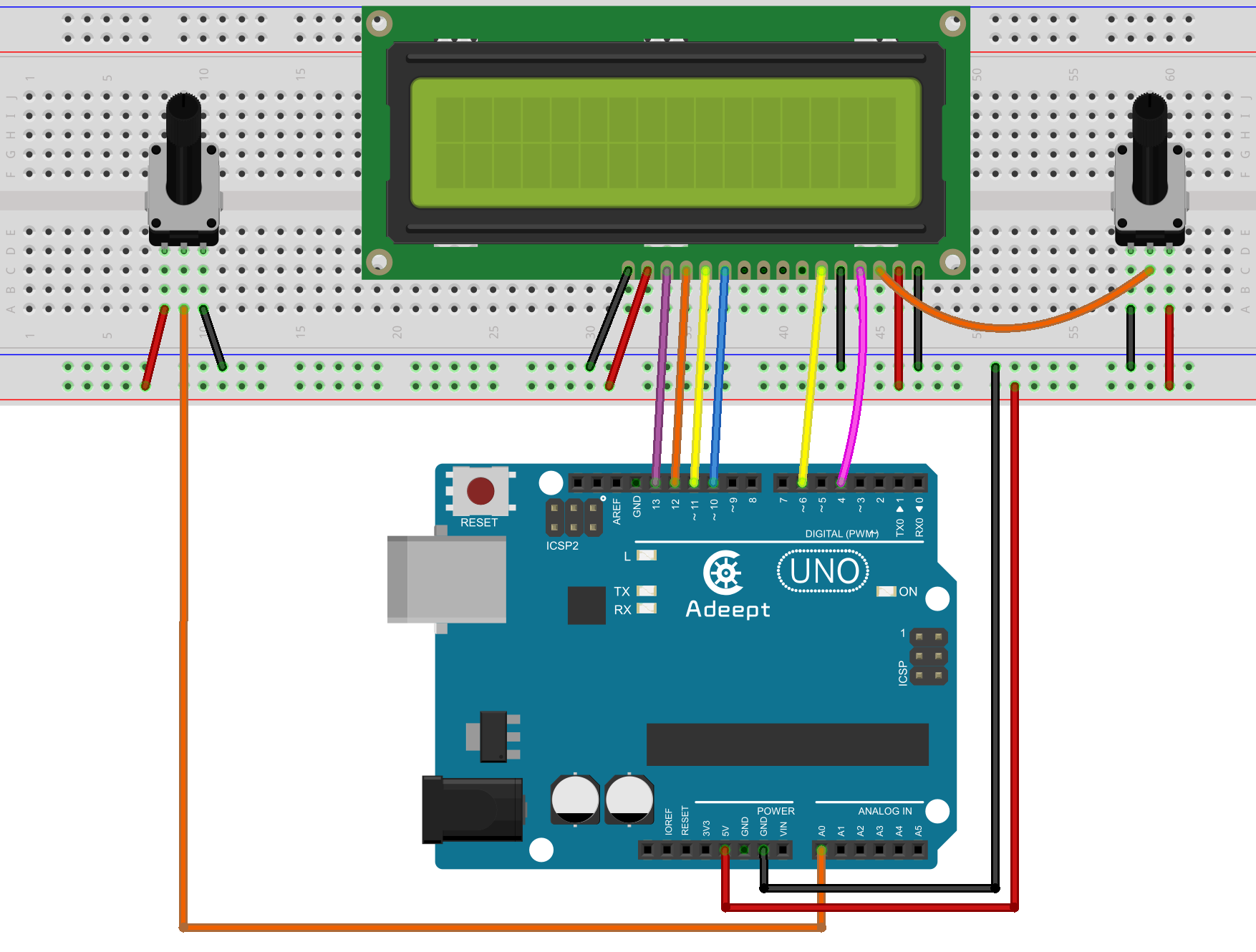
Step 2: Program
/***********************************************************
File name: 12_voltage.ino
Description: Now, when you turning the shaft of the potentiometer,
you will see the voltage displayed on the LCD1602
will be changed.
Website: www.adeept.com
E-mail: support@adeept.com
Author: Tom
Date: 2015/05/02
***********************************************************/
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
char array1[]="Adeept Voltmeter "; //the string to print on the LCD
char array2[]=" Voltage: 0.00V "; //the string to print on the LCD
// initialize the library with the numbers of the interface pins
LiquidCrystal lcd(4, 6, 10, 11, 12, 13);
int photoresistorPin = 0; // potentiometer wiper (middle terminal) connected to analog pin 3
int val=0;
int tim = 50; //the value of delay time
void setup()
{
lcd.begin(16, 2); // set up the LCD's number of columns and rows:
lcd.clear(); //Clears the LCD screen and positions the cursor in the upper-left corner
lcd.setCursor(0,0); // set the cursor to column 15, line 0
for (int positionCounter1 = 0; positionCounter1 < 16; positionCounter1++)
{
lcd.print(array1[positionCounter1]); // Print a message to the LCD.
delay(tim); //wait for 250 microseconds
}
}
void loop()
{
val = analogRead(photoresistorPin)*(5.0 / 1023.0)*100;//Data collection
array2[10] = val/100%10+0x30;//Take one hundred - bit data
array2[12] = val/10%10+0x30; //Take ten-bit data
array2[13] = val%10+0x30; //Take a bit of data
lcd.setCursor(0,1); //Set the cursor to column 15, line 1
for (int positionCounter3 = 0; positionCounter3 < 26; positionCounter3++)
{
lcd.print(array2[positionCounter3]); // Print a message to the LCD.
delay(tim); //Wait for 250 microseconds
}
}Step 3: Compile the program and upload to Arduino UNO.
Now, turn the shaft of the potentiometer, and you will see the voltage displayed on the LCD1602 changed.
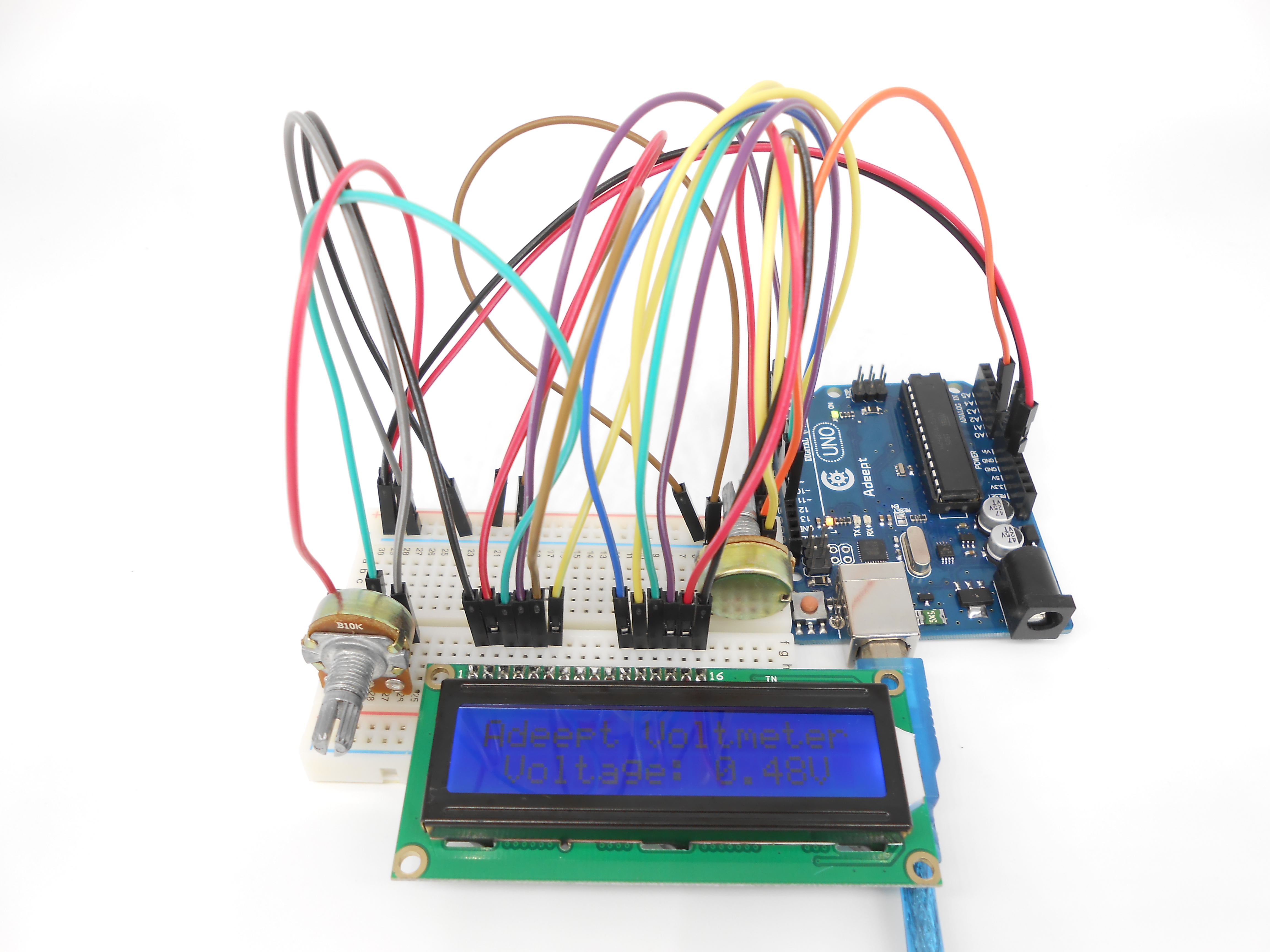
Summary
The working principle of the voltmeter is reading analog voltage which is input to the ADC inside. Through this lesson, you should have mastered how to read analog value and how to make a simple voltmeter with Arduino. Try to use the voltmeter you made and feel the charm of making!